
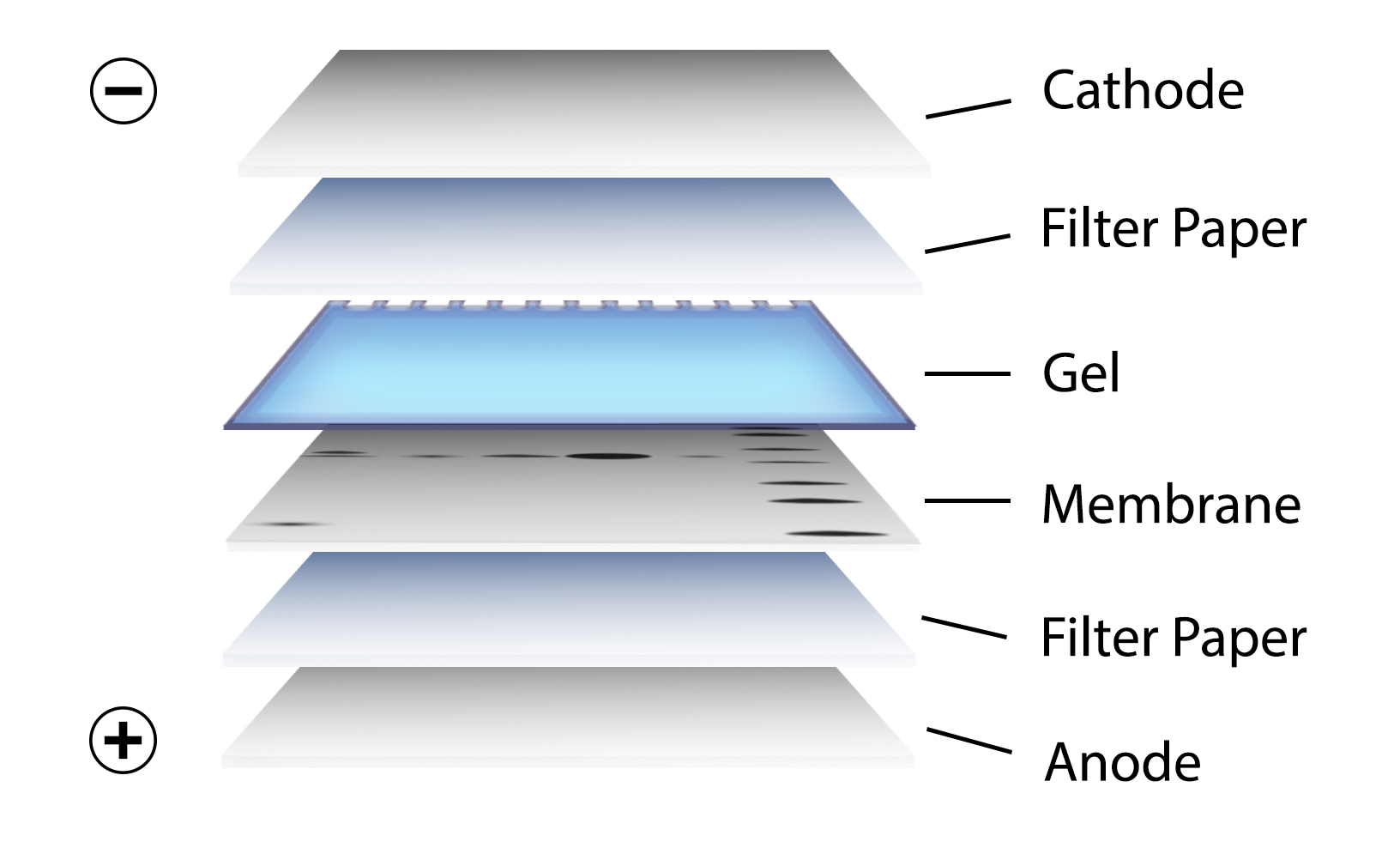
This process involves applying an electric charge to separate proteins according to their electrophoretic mobility, which depends on the structure of the proteins and their charge and molecule size. SDS-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresisīefore beginning the western blot process, researchers separate the proteins in the sample, often through SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Here, BioTechniques delves into the electrophoresis process that researchers perform to separate proteins in a sample, explains the five steps they then follow to complete the western blot, and details the control measures they can implement to generate accurate results. Western blotting has paved the way for impressive advances in scientific and medical research, which the life sciences journal BioTechniques documents in its print issues and on its multimedia website. The technique enables researchers to separate proteins by a variety of factors, label a protein of interest with an antibody, and then examine this protein. Western blotting is an analytical technique that researchers use to detect specific proteins in complex protein samples. This technique is the most widely used and has high efficiency but is messy and time consuming.A detailed insight into each stage of the western blotting process. Wet-tank transfer – the “sandwich” described above – with sponges – is placed in between two plate electrodes and submerged vertically in a chamber containing transfer buffer.There are two primary electroblotting techniques: wet tank transfer or semi-dry transfer. Since the gel and membrane are sandwiched tightly during the procedure, the proteins maintain the separation they achieved during the SDS-PAGE electrophoresis. (In wet transfer systems, there is a sponge on either side of the sandwich.) The negatively charged proteins in the gel are pulled in an electric current toward a the positively charged anode and into the membrane. A “transfer sandwich” of filter paper – gel – membrane – filter paper is placed between two electrodes. Most scientists use an electric current to transfer their proteins from gels to membrane. For most proteins, the 0.45 μm size works well, but for lower MW proteins, you should consider 0.2 μm. Membranes are available in different pore sizes, most commonly 0.2 μm and 0.45 μm. The size of the pore determines the size of the protein that can bind without passing through. The pore size of the membrane is also important. PVDF has a higher binding capacity and is stronger but needs to be activated with methanol and is more expensive.Ĭlick on the full-length article for a more in-depth comparison of these two membranes. Nitrocellulose is cheaper and has lower background but is fragile and has a lower binding capacity than PVDF. Both membranes are microporous substrates that bind proteins to their surface through hydrophobic interactions. Nitrocellulose and PVDF (polyvinylidene difluoride) are the membranes of choice for most Western blotting applications. The biggest advantages to transferring to a membrane are that membranes are easier to handle than gels and they allow for easier detection by getting the proteins out of the gel onto a thinner substrate. Transferring to a membrane makes antibody detection easier, but you need to consider which membrane to choose. This step involves incubating the transfer membrane in a solution containing an antibody to the protein of interest, and using a fluorescent tagged secondary antibody for visualization.Getting the separated proteins out of the gel and bound to a membrane allows for easier detection.Separation of the proteins in your lysate by molecular weight is done through electrophoresis. Read our lysate preparation protocol here.
You can read about our recommended lysis buffer here. To be successful, you must get your proteins out of your tissue or cells.
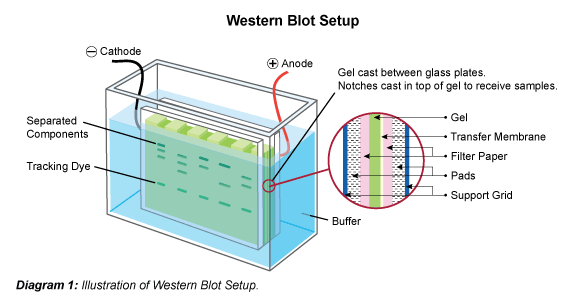
There are 4 basic steps in the Western Blot procedure. It was the third technique developed in membrane transfer, after “Southern blotting” (for DNA) and “Northern blotting” (for RNA). It was introduced in 1979 by Harry Towbin’s research lab in Switzerland. The Western Blot (or immunoblot) technique uses antibodies to detect protein targets that have been bound to a membrane. Western Blotting is a protein detection technique. Regardless of whether you perform Western blots frequently in your lab or are new to the technique, here is a reminder of (or an intro to) the fundamentals behind the box. Read the full-length piece in their website’s Education section. Our sister company, PhosphoSolutions, recently shared a blog post called " The Very Basics of Western Blotting" contributed by their own Amy Archuleta!


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
